Artificial Intelligence-Based Training System for Standardized Scanning of Pediatric Cardiac Ultrasound Standard Views
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common birth defect, with an incidence of approximately 0.9% among live births, and it constitutes a leading cause of mortality in children aged 0 to 5. In China, around 150,000 newborns are diagnosed with congenital heart disease each year, of which approximately 120,000 cases require treatment. Without timely intervention, about one-third of these infants succumb to severe complications within the first year of life. Consequently, early and accurate diagnosis of congenital heart disease is of significant clinical importance.
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) enables real-time and dynamic observation of the heart, offering advantages such as non-invasiveness, absence of radiation, and cost-effectiveness. It allows for rapid detection of various cardiac abnormalities, making it a crucial tool in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. TTE primarily involves steps like obtaining standard imaging planes, dynamic image scanning, and measurements. Accurate acquisition of standard imaging planes is a prerequisite for subsequent biometric measurements and the final diagnosis of congenital heart disease.
However, the anatomical structure and spatial configuration of the heart are complex and variable. Accurate diagnosis through TTE can be time-consuming and heavily reliant on experienced cardiac experts to make precise judgments about each ultrasound image plane. According to recommendations from the American Society of Echocardiography, standard imaging techniques are used for two-dimensional, M-mode, and color Doppler echocardiography examinations. This means that images are obtained following the same protocol in a repeatable manner. In fact, images need to be acquired in specific planes to be diagnostically useful, reducing variability between observers and within the same observer when measuring specific structures.
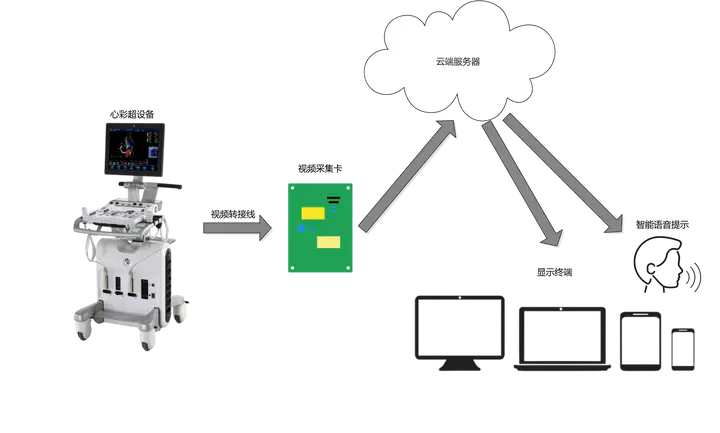
Hence, the application of deep learning technology for the automatic recognition of standard pediatric cardiac ultrasound planes is highly necessary. It serves as a foundation for intelligent diagnosis of congenital heart disease and can also be used to standardize the training of cardiac ultrasound physicians in primary healthcare institutions.
Deep learning is currently the advanced mainstream artificial intelligence technology. Applying deep learning to standardize training in pediatric cardiac ultrasound imaging is a highly clinically valuable research endeavor. This project aims to develop a system for standardizing training in pediatric cardiac ultrasound imaging.